Cystic fibrosis case study hesi – Embark on a journey into the intricacies of Cystic Fibrosis through the lens of this HESI case study. Our exploration delves into the depths of this condition, unraveling its complexities and providing a comprehensive understanding for HESI candidates.
Delve into the intricacies of Cystic Fibrosis, exploring its causes, symptoms, prevalence, and impact. We’ll dissect a patient’s medical history, unravel the diagnostic process, and scrutinize the treatment plan employed to combat this challenging condition.
Introduction
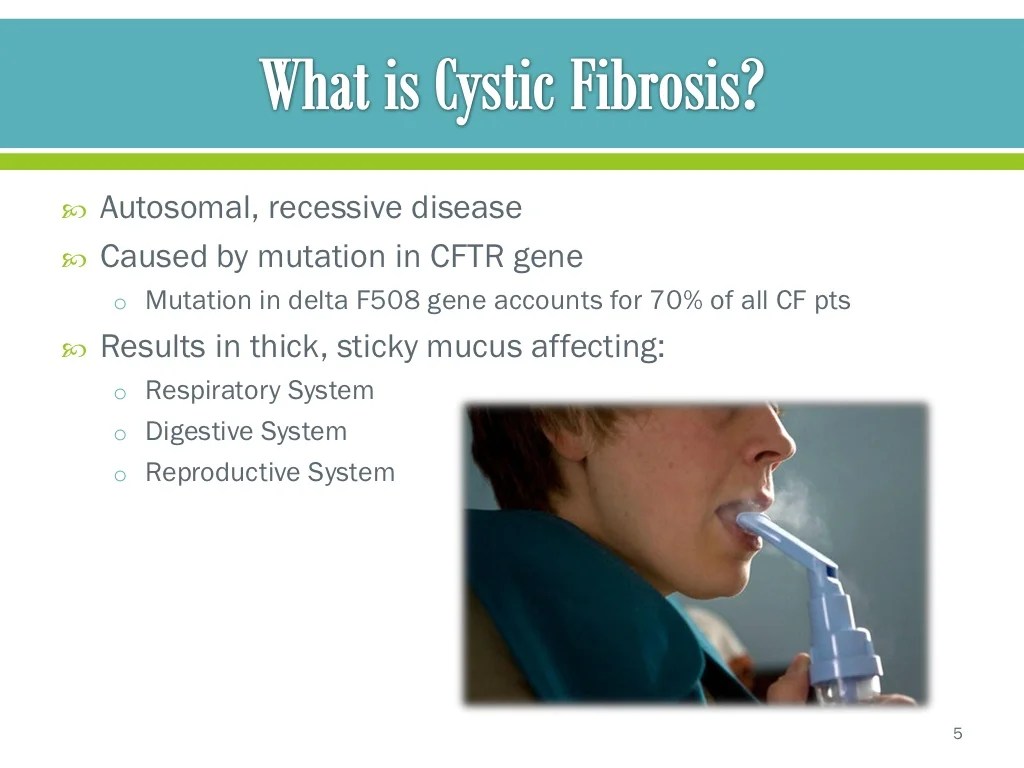
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited genetic disorder that affects the lungs, digestive system, and other organs. It is caused by a mutation in the CFTR gene, which codes for a protein that helps to regulate the flow of salt and water in and out of cells.
CF is a chronic, lifelong condition that can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Persistent coughing and wheezing
- Thick, sticky mucus that can clog the lungs and airways
- Frequent lung infections
- Difficulty breathing
- Poor growth and weight gain
- Diarrhea and constipation
- Salty-tasting skin
CF can also lead to a number of complications, including:
- Pneumonia
- Bronchitis
- Emphysema
- Diabetes
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
CF is a relatively rare condition, affecting about 1 in 3,500 people in the United States. It is more common in people of European descent. CF is a serious condition, but with proper treatment, most people with CF can live long and full lives.
Case Study: Cystic Fibrosis Case Study Hesi
Patient’s Medical History and Symptoms
The patient is a 16-year-old male with a history of chronic respiratory symptoms, including a persistent cough, wheezing, and shortness of breath. He has also experienced recurrent episodes of pneumonia and bronchitis. Additionally, he has a family history of cystic fibrosis.
Diagnostic Tests
To confirm the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis, the patient underwent several diagnostic tests, including:
- Sweat chloride test: This test measures the amount of chloride in the patient’s sweat. Elevated chloride levels are a hallmark of cystic fibrosis.
- Genetic testing: This test identifies mutations in the CFTR gene, which is responsible for cystic fibrosis.
- Chest X-ray: This imaging test can show abnormalities in the lungs, such as scarring and inflammation, which are common in cystic fibrosis.
Treatment Plan
Based on the diagnostic results, the patient was diagnosed with cystic fibrosis. His treatment plan includes:
- Bronchodilators: These medications help to open up the airways and make breathing easier.
- Antibiotics: These medications are used to treat and prevent lung infections.
- Mucolytics: These medications help to thin and loosen mucus in the lungs, making it easier to cough up.
- Nutritional support: Patients with cystic fibrosis often have difficulty absorbing nutrients from food. Nutritional support may be necessary to ensure adequate nutrition.
li>Chest physiotherapy: This therapy involves techniques to help clear mucus from the lungs.
Nursing Care
Nurses play a crucial role in the management of cystic fibrosis, providing comprehensive care that addresses the patient’s physical, emotional, and educational needs.
Nursing Interventions
Nursing interventions focus on managing the patient’s respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nutritional symptoms. These include:
- Chest physiotherapy: To clear airway secretions and improve lung function.
- Bronchodilator administration: To relax airway muscles and ease breathing.
- Antibiotic therapy: To prevent and treat lung infections.
- Pancreatic enzyme replacement: To aid in digestion and absorption of nutrients.
li>Nutritional support: To ensure adequate calorie and nutrient intake.
Education and Support
Nurses provide comprehensive education and support to the patient and family. This includes:
- Explaining the disease process and management plan.
- Teaching proper medication administration and inhaler techniques.
- Providing emotional support and counseling.
- Connecting patients with support groups and resources.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Interdisciplinary collaboration is essential in the care of patients with cystic fibrosis. Nurses work closely with:
- Physicians: To diagnose and prescribe treatment.
- Respiratory therapists: To provide chest physiotherapy and monitor lung function.
- Dietitians: To develop and monitor nutritional plans.
- Social workers: To provide emotional support and address social and economic factors.
By working together, these healthcare professionals ensure that patients receive optimal care and support to manage their condition effectively.
Pharmacotherapy

Pharmacotherapy plays a crucial role in managing cystic fibrosis (CF), aiming to improve lung function, prevent infections, and enhance overall health. Various medications are employed to address the specific challenges of CF.
Mucolytics
- Mucolytics, such as dornase alfa and hypertonic saline, help thin and loosen the thick mucus that accumulates in the airways of CF patients. This facilitates expectoration, reducing airway obstruction and improving lung function.
Bronchodilators
- Bronchodilators, such as albuterol and salmeterol, relax the muscles around the airways, making breathing easier. They are used to relieve bronchospasms and improve airflow, particularly during exacerbations.
Antibiotics
- Antibiotics are essential for treating and preventing bacterial infections in CF patients. Commonly used antibiotics include tobramycin, azithromycin, and ciprofloxacin. These medications target specific bacteria that commonly cause infections in the lungs and other organs.
Anti-inflammatory Drugs
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen and budesonide, help reduce inflammation in the airways. Inflammation is a significant contributor to CF symptoms and can lead to tissue damage. Anti-inflammatory medications aim to mitigate these effects.
Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy
- Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT) is crucial for CF patients with pancreatic insufficiency. PERT provides digestive enzymes that the pancreas fails to produce, aiding in the digestion and absorption of nutrients from food.
Importance of Medication Adherence
Medication adherence is paramount in managing CF. Regular and proper use of medications as prescribed is essential for achieving optimal outcomes. Non-adherence can lead to treatment failure, worsening of symptoms, and increased risk of complications. Therefore, healthcare providers emphasize the importance of medication adherence and provide support and guidance to patients to ensure they understand the benefits and consequences of their medications.
Respiratory Management
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a chronic, life-threatening lung disease that affects the respiratory system. It is characterized by the buildup of thick, sticky mucus in the lungs, which can lead to a number of respiratory complications.
Respiratory Complications
The most common respiratory complications associated with CF include:
- Pneumonia
- Bronchitis
- Bronchiectasis
- Pneumothorax
- Respiratory failure
Airway Clearance Techniques, Cystic fibrosis case study hesi
Airway clearance techniques are essential for managing CF and preventing respiratory complications. These techniques help to loosen and remove mucus from the lungs, making it easier to breathe.Some of the most common airway clearance techniques include:
- Chest physiotherapy (CPT)
- Airway clearance devices
- Exercise
- Coughing
Chest Physiotherapy
Chest physiotherapy (CPT) is a technique that uses manual pressure and vibration to help loosen and remove mucus from the lungs. CPT is typically performed by a physical therapist or respiratory therapist.
For a comprehensive understanding of cystic fibrosis case study hesi, a thorough grasp of human body systems is crucial. Fortunately, resources like human body systems answer key can provide invaluable insights into the interconnectedness of these systems. By exploring this resource, you can deepen your understanding of the respiratory, circulatory, and digestive systems, which play pivotal roles in cystic fibrosis case study hesi.
Airway Clearance Devices
Airway clearance devices are mechanical devices that help to loosen and remove mucus from the lungs. These devices can be used at home by patients with CF.Some of the most common airway clearance devices include:
- Oscillating positive expiratory pressure (OPEP) devices
- High-frequency chest wall oscillation (HFCWO) devices
- Intrapulmonary percussive ventilation (IPV) devices
Nutritional Management

Patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) face significant nutritional challenges due to impaired digestion and absorption of nutrients. These challenges result from the thick, sticky mucus that accumulates in the lungs and digestive tract, interfering with the normal functioning of the digestive system.
To address these challenges, dietary modifications and supplements are recommended for CF patients. These modifications include:
Dietary Modifications
- High-calorie diet:CF patients require a high-calorie diet (25-50% more calories than healthy individuals) to compensate for increased energy expenditure and malabsorption.
- High-fat diet:Fat is an important source of energy for CF patients, as it is easier to digest and absorb than other nutrients.
- Increased protein intake:Protein is essential for growth, repair, and immune function. CF patients need more protein than healthy individuals to maintain muscle mass and prevent malnutrition.
- Adequate vitamin and mineral intake:CF patients may have difficulty absorbing certain vitamins and minerals, such as fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and calcium. Supplementation may be necessary to ensure adequate intake.
- Reduced fiber intake:Fiber can be difficult to digest for CF patients, as it can further thicken mucus and block the digestive tract.
Supplements
- Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT):PERT is a combination of enzymes that help break down food and aid in digestion. It is essential for CF patients who have insufficient pancreatic function.
- Vitamin and mineral supplements:As mentioned earlier, CF patients may require supplementation of certain vitamins and minerals to ensure adequate intake.
Nutritional support is crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of CF patients. By addressing the nutritional challenges they face, healthcare professionals can help these patients achieve optimal growth, development, and quality of life.
Psychological and Social Impact
Cystic fibrosis (CF) significantly impacts the psychological and social well-being of patients and their families.
Patients often face chronic pain, isolation, and anxiety due to their condition. Social stigma and misconceptions can further exacerbate their emotional distress.
Role of Support Groups and Counseling
Support groups provide a safe and supportive environment where patients and families can connect with others who understand their challenges.
Counseling can help patients cope with the emotional burden of CF, develop coping mechanisms, and improve their quality of life.
Importance of Addressing Mental Health Needs
Addressing the mental health needs of patients and families is crucial for their overall well-being.
Mental health support can help reduce anxiety, depression, and isolation, enabling patients and families to live more fulfilling lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary cause of Cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic Fibrosis is primarily caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, which encodes a protein responsible for regulating the flow of salt and water across cell membranes.
How common is Cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic Fibrosis is a relatively rare condition, affecting approximately 1 in 3,000 newborns in the United States.
What are the most common symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis?
Common symptoms include persistent coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, salty-tasting skin, and digestive issues such as diarrhea and constipation.