Patterns of Natural Selection Worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamental principles and mechanisms that drive the process of evolution. This in-depth resource delves into the intricate workings of natural selection, exploring its role in shaping the diversity of life on Earth.
Natural selection, as Artikeld in this worksheet, is a driving force behind the adaptation and diversification of species over time. It acts as a selective pressure, favoring individuals with advantageous traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success within a given environment.
Patterns of Natural Selection
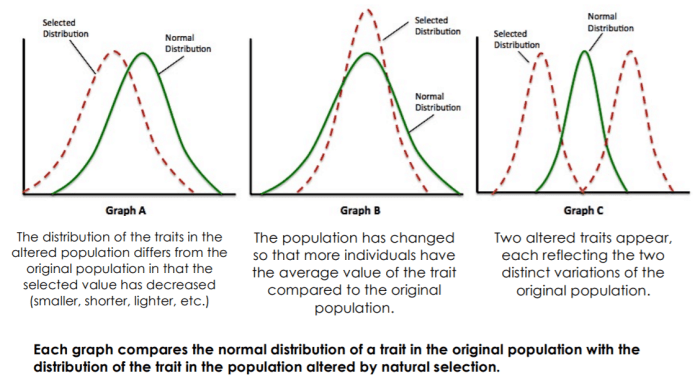
Natural selection, a cornerstone of evolutionary theory, drives the adaptation and diversification of species. This process involves the selective survival and reproduction of individuals with traits that enhance their fitness in a particular environment. Over time, natural selection can lead to significant changes in species’ genetic makeup and phenotypic characteristics.
Patterns of natural selection provide valuable insights into the evolutionary processes shaping the diversity of life on Earth. These patterns include:
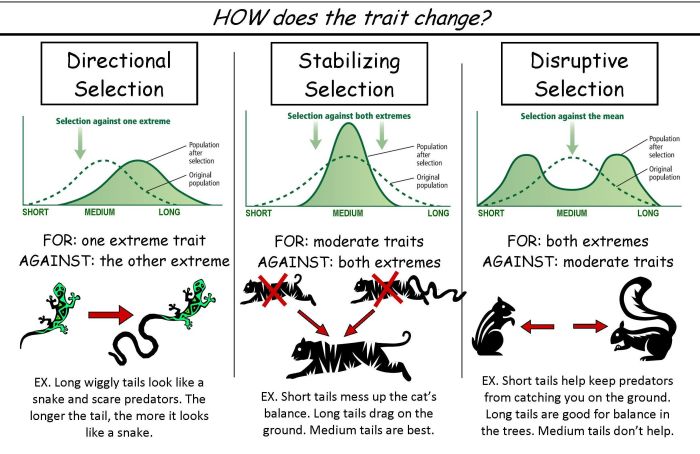
Types of Natural Selection
- Stabilizing selection:Favors intermediate phenotypes, maintaining genetic diversity and stabilizing traits within a population.
- Directional selection:Drives the population towards a specific extreme phenotype, often in response to environmental changes.
- Disruptive selection:Selects for extreme phenotypes at both ends of the spectrum, leading to the formation of distinct subpopulations or new species.
Factors Influencing Natural Selection, Patterns of natural selection worksheet
The rate and direction of natural selection are influenced by several factors:
- Environmental pressures:Changes in the environment, such as resource availability or predation, can drive natural selection.
- Genetic variation:The presence of genetic variation within a population provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon.
- Population size:Smaller populations are more susceptible to genetic drift, which can hinder natural selection.
Examples of Natural Selection Patterns
Common patterns of natural selection include:
- Antibiotic resistance:Bacteria evolve resistance to antibiotics, driven by selective survival of individuals with resistance genes.
- Speciation:Natural selection can lead to the formation of new species through reproductive isolation and genetic divergence.
- Convergent evolution:Unrelated species develop similar adaptations to similar environmental pressures, resulting in analogous structures.
Applications of Natural Selection
Understanding natural selection has practical applications in various fields:
- Medicine:Identifying the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance and developing new treatments.
- Agriculture:Breeding crops and livestock with desirable traits through selective breeding.
- Conservation biology:Protecting endangered species by understanding the selective pressures they face.
General Inquiries: Patterns Of Natural Selection Worksheet
What is the significance of natural selection in shaping the diversity of life on Earth?
Natural selection plays a pivotal role in driving the diversification of life on Earth. It acts as a selective force, favoring individuals with advantageous traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success within their environment. Over time, this process leads to the accumulation of genetic changes within populations, resulting in the emergence of new species and the adaptation of existing ones to changing environmental conditions.
How do different types of natural selection contribute to evolutionary outcomes?
Natural selection operates through various mechanisms, each contributing to distinct evolutionary outcomes. Stabilizing selection maintains the average trait value within a population, directional selection favors a shift in the average trait value, and disruptive selection promotes the divergence of a population into two or more distinct groups.
Understanding the different types of natural selection is crucial for comprehending the diverse patterns of evolution observed in nature.
What factors influence the rate and direction of natural selection?
The rate and direction of natural selection are influenced by a combination of factors, including environmental pressures, genetic variation, and population size. Environmental pressures, such as predation, competition, and resource availability, exert selective forces on individuals. Genetic variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon, and population size affects the strength of selection and the rate of evolutionary change.