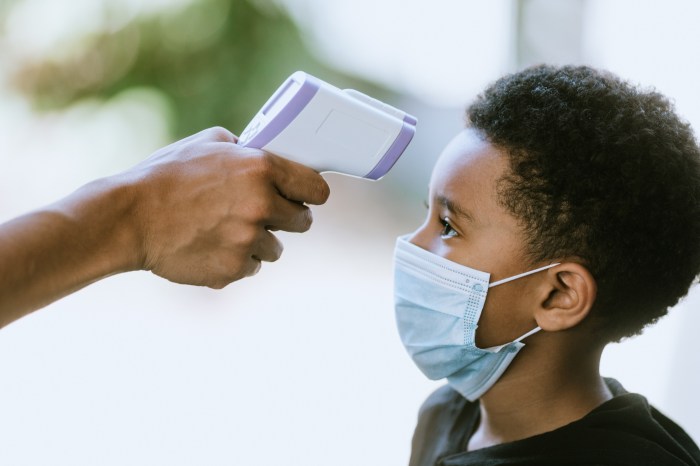
Why would you use an infrared thermometer? The answer lies in their unique capabilities and the benefits they offer in various fields. Infrared thermometers measure temperature without physical contact, making them ideal for scenarios where traditional methods are impractical or pose safety risks.
Let’s explore the diverse applications and advantages of infrared thermometers.
From industrial settings to healthcare facilities, infrared thermometers provide accurate and efficient temperature readings. They are particularly valuable in situations where non-contact measurement is crucial, such as detecting fevers, monitoring industrial processes, and ensuring product quality.
Infrared Thermometer Overview: Why Would You Use An Infrared Thermometer
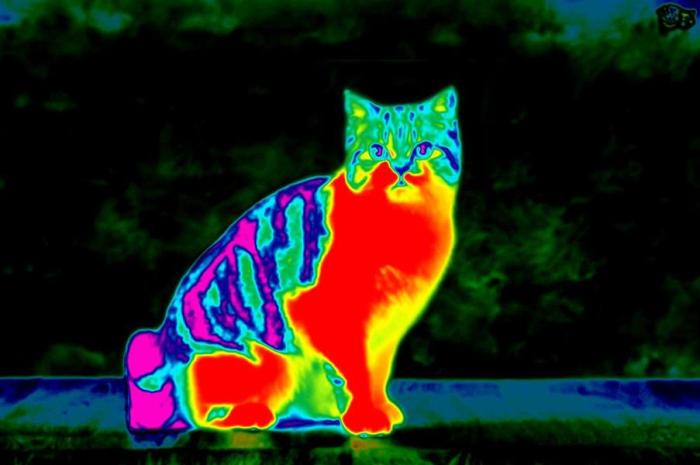

Infrared thermometers are non-contact devices that measure the surface temperature of objects by detecting the infrared radiation they emit. They utilize infrared sensors to convert the detected radiation into an electrical signal, which is then processed to display the temperature reading.
Compared to traditional contact thermometers, infrared thermometers offer several advantages, including:
- Non-contact measurement, eliminating the need for physical contact and reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
- Fast and accurate temperature readings, making them ideal for quick and efficient temperature monitoring.
- Wide temperature range, allowing them to measure temperatures from extreme cold to extreme heat.
- Versatile applications, suitable for various industries and scenarios, including healthcare, industrial settings, and household use.
Applications of Infrared Thermometers
Infrared thermometers find extensive applications in various industries and scenarios, including:
- Healthcare:Fever detection, temperature monitoring, infection control, and patient safety.
- Industrial:Quality control, process monitoring, equipment maintenance, and energy efficiency.
- Household:Cooking, food safety, HVAC maintenance, and energy conservation.
- Automotive:Engine diagnostics, brake temperature monitoring, and tire temperature measurement.
- Research and Development:Material testing, thermal analysis, and non-destructive testing.
Non-Contact Temperature Measurement, Why would you use an infrared thermometer
The non-contact nature of infrared thermometers offers significant advantages, particularly in scenarios where physical contact is impractical or poses a safety risk. By measuring temperature from a distance, infrared thermometers:
- Eliminate the need for direct contact, preventing cross-contamination and the spread of pathogens.
- Allow for safe temperature measurement of hazardous or inaccessible objects, such as high-voltage equipment or moving machinery.
- Enable rapid temperature screening of large groups of people, making them ideal for fever detection and public health monitoring.
Safety and Convenience
Infrared thermometers enhance safety and convenience in various ways:
- Safety:Non-contact measurement eliminates the risk of burns, electrical shock, or exposure to hazardous substances.
- Convenience:Easy to use, requiring minimal training and no physical contact with the object being measured.
- Portability:Compact and lightweight, making them suitable for field measurements and on-the-go applications.
Temperature Range and Accuracy
Infrared thermometers have a wide temperature range, typically from -50°C to 1000°C or higher, making them suitable for various applications. The accuracy of infrared thermometers varies depending on factors such as the quality of the sensor, the distance from the object, and the emissivity of the object’s surface.
High-quality infrared thermometers can achieve accuracies of ±1°C or better.
Applications in Healthcare
Infrared thermometers play a crucial role in healthcare settings, particularly in:
- Fever detection:Rapid and non-invasive temperature screening for fever detection.
- Temperature monitoring:Continuous temperature monitoring of patients in critical care units or during surgery.
- Infection control:Identifying individuals with elevated temperatures, helping to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
- Patient safety:Ensuring patient safety by monitoring body temperature and detecting potential infections.
Industrial Applications
Infrared thermometers are widely used in industrial settings for:
- Quality control:Verifying the temperature of products during manufacturing to ensure quality standards.
- Process monitoring:Monitoring the temperature of processes and equipment to optimize efficiency and prevent overheating.
- Equipment maintenance:Identifying overheating or malfunctioning components, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Energy efficiency:Detecting energy losses and identifying areas for improvement in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
Design and Features
Infrared thermometers come in various designs and feature sets to meet specific application requirements. Common features include:
- Size and shape:Compact and handheld designs for portability and ease of use.
- Display options:LCD or LED displays with backlighting for clear and convenient readings.
- Emissivity settings:Adjustable emissivity settings to ensure accurate temperature readings for different surface materials.
- Data storage and retrieval:Some models offer data storage and retrieval capabilities for record-keeping and analysis.
- Connectivity:Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connectivity for data transfer and remote monitoring.
Top FAQs
What are the advantages of using infrared thermometers?
Infrared thermometers offer several advantages, including non-contact measurement, reduced risk of cross-contamination, safety in hazardous environments, and ease of use.
How accurate are infrared thermometers?
The accuracy of infrared thermometers varies depending on the model and manufacturer. However, they generally provide reliable temperature readings within a specific range.
What are some common applications of infrared thermometers?
Infrared thermometers are widely used in healthcare for fever detection and temperature monitoring, as well as in industrial settings for quality control, process monitoring, and equipment maintenance.