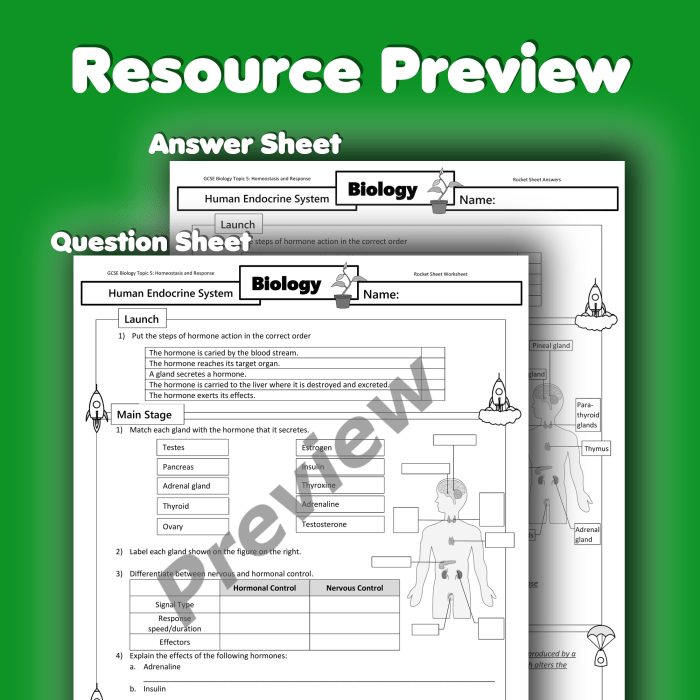
Endocrine system interactive activity answers – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of endocrinology with our comprehensive answers to the endocrine system interactive activity. Delve into the intricate workings of the endocrine system, unraveling the mysteries of hormone regulation and its profound impact on our bodies.
As we navigate through this interactive exploration, we will illuminate the functions of major endocrine glands, dissect the mechanisms of hormone regulation, and shed light on common endocrine disorders. Prepare to be enlightened as we unravel the intricate tapestry of the endocrine system, empowering you with a deeper understanding of its vital role in maintaining our health and well-being.
Endocrine System Overview
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and secrete hormones, which are chemical messengers that regulate various bodily functions. Hormones travel through the bloodstream to target specific cells and tissues, controlling a wide range of processes, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood.
Hormones act as signals that coordinate and integrate different organs and systems in the body, maintaining homeostasis and ensuring optimal functioning.
Major Endocrine Glands
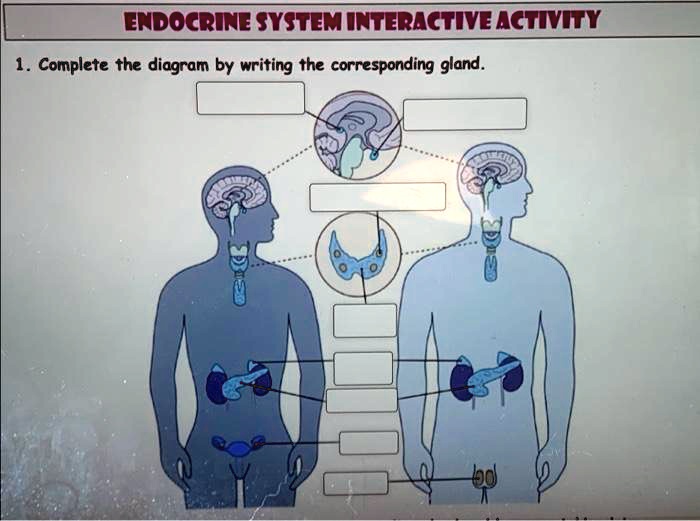
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain, is often referred to as the “master gland” as it controls the activity of many other endocrine glands.
Hormones produced:
- Growth hormone (GH)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, produces hormones that regulate metabolism and energy levels.
Hormones produced:
- Thyroxine (T4)
- Triiodothyronine (T3)
Parathyroid Glands
The parathyroid glands, located near the thyroid gland, produce hormones that regulate calcium levels in the body.
Hormones produced:
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Adrenal Glands
The adrenal glands, located above the kidneys, produce hormones that regulate stress responses and blood pressure.
Hormones produced:
- Cortisol
- Epinephrine (adrenaline)
- Norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
Pancreas
The pancreas, located behind the stomach, produces hormones that regulate blood sugar levels.
Hormones produced:
- Insulin
- Glucagon
Hormone Regulation and Feedback Mechanisms: Endocrine System Interactive Activity Answers
Hormone levels are tightly regulated through feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis in the body.
Negative Feedback Loops
In a negative feedback loop, the hormone produced by the endocrine gland inhibits its own production or the production of other hormones that stimulate it. This mechanism helps to prevent overproduction of hormones and maintain a steady state.
Positive Feedback Loops
In a positive feedback loop, the hormone produced by the endocrine gland stimulates its own production or the production of other hormones that stimulate it. This mechanism is less common but is essential for certain processes, such as childbirth.
Endocrine Disorders

Disruptions in the endocrine system can lead to various disorders, including:
Diabetes, Endocrine system interactive activity answers
Diabetes is a condition in which the body cannot produce or effectively use insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders include hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), which can cause a range of symptoms, including weight changes, fatigue, and changes in heart rate.
Cushing’s Syndrome
Cushing’s syndrome is a condition caused by excessive production of cortisol, which can lead to weight gain, high blood pressure, and muscle weakness.
FAQ
What is the primary function of the endocrine system?
The endocrine system is responsible for regulating and coordinating various bodily functions through the production and secretion of hormones.
Name the major endocrine glands and their respective hormones.
The major endocrine glands include the pituitary gland (growth hormone, prolactin), thyroid gland (thyroxine, triiodothyronine), parathyroid glands (parathyroid hormone), adrenal glands (adrenaline, cortisol), and pancreas (insulin, glucagon).
Explain the concept of negative feedback loops in hormone regulation.
Negative feedback loops are regulatory mechanisms in which the output of a system inhibits the input, maintaining hormone levels within a specific range. For example, when blood glucose levels rise, the pancreas releases insulin to lower them, and when blood glucose levels fall, the pancreas releases glucagon to raise them.