The tuberculin skin test _______. select all that apply. – The tuberculin skin test, a crucial diagnostic tool in the fight against tuberculosis, offers valuable insights into infection status and guides treatment decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the test, exploring its purpose, procedure, interpretation, limitations, and role in tuberculosis management.
The Tuberculin Skin Test
The tuberculin skin test is a medical procedure used to determine if a person has been exposed to the bacteria that causes tuberculosis (TB). It is a simple and inexpensive test that has been used for over a century to diagnose TB infection.The
tuberculin skin test is typically used to screen people who are at high risk for developing TB, such as healthcare workers, people who live in or have traveled to areas where TB is common, and people who have weakened immune systems.
It can also be used to monitor people who are being treated for TB to ensure that the treatment is effective.
Procedure for the Tuberculin Skin Test
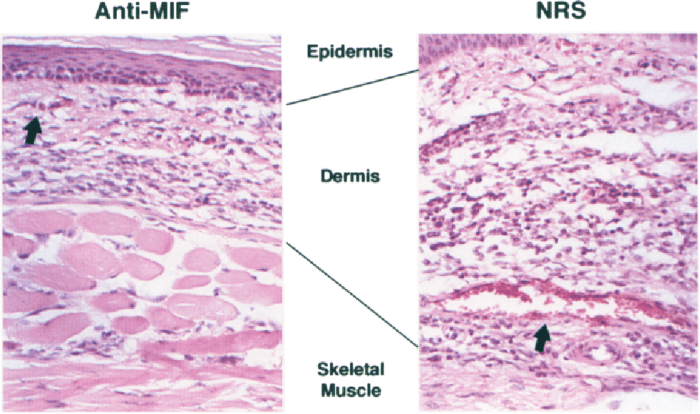
The tuberculin skin test is administered by injecting a small amount of tuberculin, a purified protein derivative (PPD) of the TB bacteria, into the skin of the forearm. The injection site is then checked 48 to 72 hours later for a reaction.A
positive reaction to the tuberculin skin test indicates that the person has been exposed to the TB bacteria and has developed an immune response to it. The size of the reaction is used to determine the severity of the infection.
Interpretation of the Tuberculin Skin Test Results, The tuberculin skin test _______. select all that apply.
The tuberculin skin test results are interpreted based on the size of the reaction at the injection site. A reaction of 5 mm or more is considered positive in people who are at high risk for developing TB. A reaction of 10 mm or more is considered positive in people who are at low risk for developing TB.A
negative reaction to the tuberculin skin test indicates that the person has not been exposed to the TB bacteria or has not developed an immune response to it. However, a negative reaction does not rule out the possibility of TB infection, especially in people who are immunocompromised.
Limitations and Considerations of the Tuberculin Skin Test
The tuberculin skin test is a valuable tool for diagnosing TB infection, but it has some limitations. The test can produce false-positive results in people who have been vaccinated against TB or who have been exposed to other mycobacteria, such as those that cause leprosy.
The test can also produce false-negative results in people who are immunocompromised or who have recently been infected with TB.It is important to note that the tuberculin skin test is not a perfect test and should not be used as the sole basis for diagnosing or excluding TB infection.
Other tests, such as chest X-rays and sputum cultures, may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Role of the Tuberculin Skin Test in Diagnosis and Management
The tuberculin skin test is a valuable tool for diagnosing TB infection and monitoring treatment. It can help to identify people who are at high risk for developing TB and who need to be treated. The test can also be used to monitor people who are being treated for TB to ensure that the treatment is effective.
Alternatives to the Tuberculin Skin Test
There are several alternative methods for testing for TB infection, including:
- Interferon gamma release assays (IGRAs)
- Chest X-rays
- Sputum cultures
IGRAs are blood tests that measure the body’s immune response to TB bacteria. They are more specific than the tuberculin skin test and are not affected by vaccination or exposure to other mycobacteria. Chest X-rays can be used to detect TB infection in the lungs.
Sputum cultures can be used to diagnose TB infection in people who are coughing up sputum.
Question Bank: The Tuberculin Skin Test _______. Select All That Apply.
What is the purpose of the tuberculin skin test?
The tuberculin skin test is used to detect previous or current infection with the bacteria that cause tuberculosis (TB).
How is the tuberculin skin test performed?
A small amount of tuberculin, a purified protein derivative from TB bacteria, is injected into the skin of the forearm. The site is then observed for a reaction, typically within 48-72 hours.
How is the tuberculin skin test interpreted?
The size of the reaction at the injection site determines the result. A positive result indicates previous or current TB infection, while a negative result suggests no exposure or a non-reactive immune system.