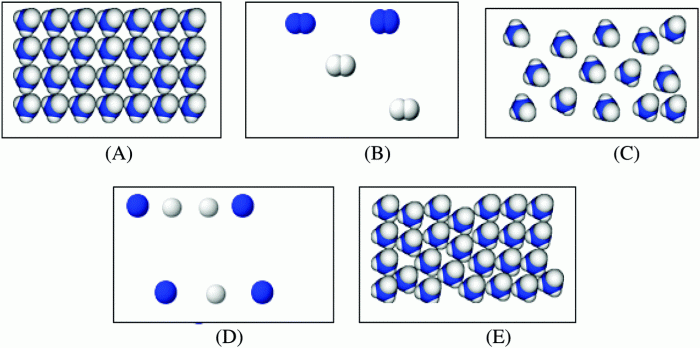
Which diagram best represents a gas in a closed container – Delving into the realm of gases confined within closed containers, this article embarks on a comprehensive analysis to determine which diagram most aptly captures the essence of this physical phenomenon. By exploring the properties of gases, the nature of closed containers, and the behavior of gas particles within such systems, we will illuminate the diagram that best represents the intricate dynamics at play.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we will examine various types of diagrams commonly employed to depict gases in closed containers, including Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Diagrams, Particle Distribution Diagrams, Pressure-Volume (P-V) Diagrams, and Temperature-Volume (T-V) Diagrams. Through a meticulous comparison of these diagrams, we will assess their ability to represent particle movement, pressure and volume relationships, and temperature and volume relationships within closed gas systems.
Which Diagram Best Represents a Gas in a Closed Container
Introduction
A gas is a state of matter characterized by its fluidity and ability to expand to fill its container. In a closed container, gas particles are confined and interact with each other and the container walls.
This article aims to determine which diagram best represents the behavior of a gas in a closed container. We will examine different types of diagrams, their advantages and disadvantages, and their ability to represent various aspects of gas behavior.
Types of Diagrams, Which diagram best represents a gas in a closed container
Various types of diagrams are used to represent gases in closed containers, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
| Diagram Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Diagram | Shows gas particles as point masses moving randomly and colliding with each other and the container walls. | – Visually represents particle movement and collisions. | – Does not show particle distribution or pressure-volume relationships. |
| Particle Distribution Diagram | Shows the distribution of gas particles in a container, indicating regions of higher or lower concentration. | – Illustrates particle distribution and density variations. | – Does not show particle movement or pressure-volume relationships. |
| Pressure-Volume (P-V) Diagram | Plots pressure against volume, showing the relationship between these variables. | – Clearly shows pressure-volume relationships. | – Does not show particle movement or distribution. |
| Temperature-Volume (T-V) Diagram | Plots temperature against volume, showing the relationship between these variables. | – Clearly shows temperature-volume relationships. | – Does not show particle movement or distribution. |
Gas Behavior in Closed Containers
In a closed container, gas particles move randomly and collide with each other and the container walls. These collisions create pressure, which is the force exerted by the gas particles on the container walls. The volume of the gas is determined by the size of the container, and the temperature of the gas is determined by the average kinetic energy of its particles.
Comparison of Diagrams
To determine the most suitable diagram for representing a gas in a closed container, we will compare their ability to represent the following aspects:
- Particle movement and distribution
- Pressure and volume relationships
- Temperature and volume relationships
| Diagram Type | Particle Movement and Distribution | Pressure and Volume Relationships | Temperature and Volume Relationships |
|---|---|---|---|
| KMT Diagram | Good | Poor | Poor |
| Particle Distribution Diagram | Good | Poor | Poor |
| P-V Diagram | Poor | Good | Poor |
| T-V Diagram | Poor | Poor | Good |
Selection of Best Diagram
Based on the comparison above, the Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Diagram is the most suitable for representing a gas in a closed container. This diagram provides a good representation of particle movement and distribution, which are key aspects of gas behavior in a closed system.
While the P-V and T-V diagrams provide valuable information about pressure-volume and temperature-volume relationships, they do not provide a clear representation of particle movement and distribution.
It is important to note that the KMT diagram has limitations. It does not show the actual size or shape of gas particles, and it does not accurately represent the forces between particles. However, it provides a useful conceptual model for understanding the behavior of gases in closed containers.
FAQ Section: Which Diagram Best Represents A Gas In A Closed Container
What is the primary objective of this analysis?
The primary objective is to determine which diagram best represents the behavior of a gas in a closed container.
What factors are considered when comparing different diagrams?
The diagrams are compared based on their ability to represent particle movement, pressure and volume relationships, and temperature and volume relationships.
Why is the Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) Diagram considered the most suitable choice?
The KMT Diagram provides a comprehensive representation of gas behavior, including particle motion, collisions, and relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature.