HESI case study ectopic pregnancy delves into the intricate world of ectopic pregnancy, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and management strategies. This case study provides a comprehensive analysis of a real-life scenario, offering valuable insights for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to understand this critical condition.
Ectopic pregnancy, a life-threatening condition, occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. This case study explores the complexities of diagnosing and treating ectopic pregnancy, highlighting the importance of prompt medical intervention.
Introduction
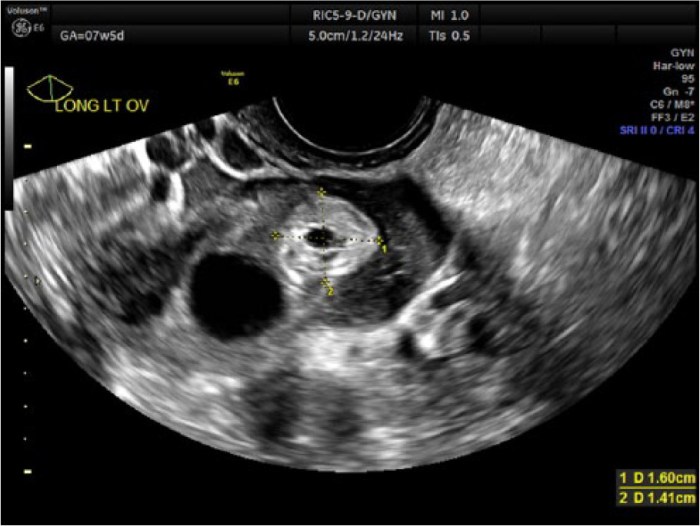
This case study examines an ectopic pregnancy, a life-threatening condition where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. It aims to enhance the understanding of ectopic pregnancy, its diagnosis, management, and implications for clinical practice.
Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency, accounting for approximately 2% of all pregnancies. It occurs when the fertilized egg implants in the fallopian tube, ovary, or cervix, rather than the uterus. Symptoms may include pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding, and irregular menstrual cycles.
Risk factors include previous ectopic pregnancy, pelvic inflammatory disease, and assisted reproductive technologies.
Case Presentation
A 32-year-old female presented with a 2-week history of lower abdominal pain and irregular vaginal bleeding. She had a history of pelvic inflammatory disease and was currently undergoing fertility treatment. Physical examination revealed tenderness in the left lower quadrant and a positive pregnancy test.
Transvaginal ultrasound showed an empty uterus and a complex mass in the left adnexa. Blood tests confirmed elevated beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG) levels. Differential diagnoses included ectopic pregnancy, corpus luteum cyst, and ovarian torsion. Laparoscopy was performed, confirming an ectopic pregnancy in the left fallopian tube.
Management: Hesi Case Study Ectopic Pregnancy
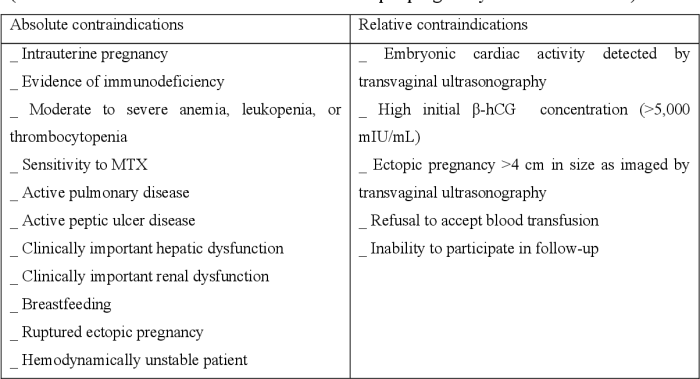
Treatment options for ectopic pregnancy include medical management with methotrexate and surgical intervention. Methotrexate is a chemotherapeutic agent that inhibits cell division, leading to the regression of the ectopic pregnancy. Surgical intervention involves laparoscopy or laparotomy to remove the ectopic pregnancy.
In this case, laparoscopic salpingectomy was performed to remove the affected fallopian tube. This approach was chosen due to the patient’s desire for future fertility and the high risk of tubal rupture.
Potential complications associated with the treatment include bleeding, infection, and damage to adjacent organs. In this case, the patient experienced minimal complications and recovered well.
Outcomes

The patient’s beta-hCG levels normalized postoperatively, and she was discharged from the hospital. Follow-up ultrasound confirmed the resolution of the ectopic pregnancy. The patient has not experienced any further complications and is currently undergoing fertility treatments.
Discussion
This case highlights the importance of early diagnosis and prompt treatment of ectopic pregnancy. The patient’s symptoms and medical history raised suspicion for an ectopic pregnancy, and timely intervention prevented life-threatening complications.
The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the patient’s clinical presentation, the location of the ectopic pregnancy, and the patient’s desire for future fertility. Laparoscopic salpingectomy is a safe and effective treatment option for ectopic pregnancies in stable patients.
This case also underscores the need for continued research to improve the diagnosis and management of ectopic pregnancy. Identifying novel biomarkers and developing minimally invasive treatment techniques could further enhance patient outcomes.
Top FAQs
What are the risk factors for ectopic pregnancy?
Risk factors include pelvic inflammatory disease, previous ectopic pregnancy, and assisted reproductive technologies.
How is ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examination, ultrasound, and blood tests.
What are the treatment options for ectopic pregnancy?
Treatment options include medical management with methotrexate or surgical intervention, such as laparoscopy or laparotomy.