Embark on a scientific journey with Mendel’s pea plants worksheet answer key, where the foundational principles of genetics unfold. Through meticulous experiments and insightful analysis, Gregor Mendel’s groundbreaking work laid the groundwork for our understanding of inheritance and genetic traits.
Delve into the fascinating world of pea plants, where dominant and recessive alleles dance in intricate patterns, shaping the visible characteristics we observe. Punnett squares become your tools to predict the probabilities of offspring genotypes and phenotypes, empowering you to unravel the mysteries of genetic inheritance.
Introduction
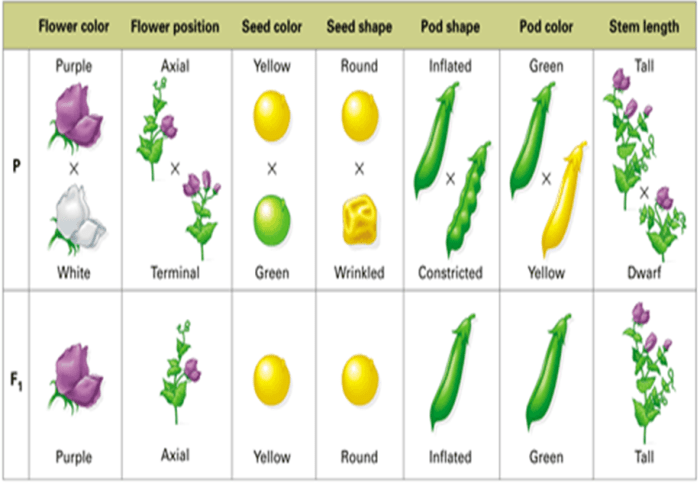
Gregor Mendel, a 19th-century Austrian monk, conducted groundbreaking experiments with pea plants that laid the foundation for the field of genetics. Mendel’s experiments revealed the basic principles of inheritance, which have since become known as Mendelian genetics.
Mendelian inheritance is based on the idea that each trait is controlled by two alleles, one inherited from each parent. The alleles can be dominant or recessive. A dominant allele will always be expressed in the phenotype, regardless of the presence of the recessive allele.
A recessive allele will only be expressed in the phenotype if both alleles are recessive.
Punnett Squares
A Punnett square is a diagram that is used to predict the probability of offspring genotypes and phenotypes. The Punnett square is constructed by listing the possible alleles for each parent on the sides of the square. The possible offspring genotypes are then listed in the boxes of the square.
For example, if a pea plant with the genotype Aa is crossed with a pea plant with the genotype aa, the Punnett square would look like this:
| A | a | |
|---|---|---|
| a | Aa | aa |
| a | Aa | aa |
The Punnett square shows that there is a 50% chance that the offspring will be Aa and a 50% chance that the offspring will be aa.
Dominant and Recessive Alleles
Dominant alleles are alleles that are expressed in the phenotype regardless of the presence of the recessive allele. Recessive alleles are alleles that are only expressed in the phenotype if both alleles are recessive.
In pea plants, the allele for tall stems is dominant over the allele for short stems. This means that a pea plant with the genotype Tt will have tall stems, even though it has one recessive allele for short stems.
Genotypes and Phenotypes
The genotype of an organism is the genetic makeup of the organism. The phenotype of an organism is the observable characteristics of the organism.
The genotype of an organism determines the phenotype of the organism. However, the phenotype of an organism can also be influenced by environmental factors.
Dihybrid Crosses
A dihybrid cross is a cross between two individuals that are heterozygous for two different genes. The Punnett square for a dihybrid cross is more complex than the Punnett square for a monohybrid cross because it takes into account the possible combinations of alleles for both genes.
For example, if a pea plant with the genotype AaBb is crossed with a pea plant with the genotype AaBb, the Punnett square would look like this:
| AB | Ab | aB | ab | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | AABB | AABb | AaBB | AaBb |
| Ab | AABb | AAbb | AaBb | Aabb |
| aB | AaBB | AaBb | aaBB | aaBb |
| ab | AaBb | Aabb | aaBb | aabb |
The Punnett square shows that there are 9 possible offspring genotypes and 4 possible offspring phenotypes.
Independent Assortment, Mendel’s pea plants worksheet answer key
Independent assortment is the principle that the alleles of different genes are inherited independently of each other. This means that the genotype of an organism for one gene does not affect the genotype of the organism for another gene.
Independent assortment is one of the reasons why there is so much genetic variation in the population.
Applications of Mendelian Genetics
Mendelian genetics has a wide range of applications in agriculture, medicine, and forensics.
- In agriculture, Mendelian genetics is used to improve the yield and quality of crops.
- In medicine, Mendelian genetics is used to diagnose and treat genetic diseases.
- In forensics, Mendelian genetics is used to identify criminals and to determine paternity.
Limitations of Mendelian Genetics
Mendelian genetics is a powerful tool, but it has some limitations.
- Mendelian genetics does not take into account the effects of environmental factors on the phenotype of an organism.
- Mendelian genetics does not take into account the effects of mutations.
- Mendelian genetics does not take into account the effects of gene interactions.
Question Bank: Mendel’s Pea Plants Worksheet Answer Key
What is the significance of Mendel’s pea plant experiments?
Mendel’s experiments established the fundamental principles of Mendelian inheritance, providing a framework for understanding the transmission of genetic traits from parents to offspring.
How do Punnett squares aid in predicting offspring genotypes?
Punnett squares are graphical tools that help determine the possible combinations of alleles inherited from parents, allowing us to predict the probability of specific genotypes in offspring.
What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype?
A genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, while a phenotype describes the observable characteristics that result from the interaction between the genotype and the environment.